《战争雷霆》弹种问题分析及损伤原理一览!


对于战争雷霆游戏中有很多子弹的介绍,刚上手来说可能比较不知所措,在没有实际使用的情况下,也不知道那种子弹的威力最大,所以小熊北北今天总结了下关于子弹种类以及损伤机制原理分析的文章,希望有需要的玩家可以认真看看。按照惯例,对于长篇大论看不下去的玩家,我首先给出全文的结论图。希望你们也可以根据结论图去找寻自己希望得到的攻略。
(下图,T是指曳光弹,F是指碎片弹,HE是指高爆弹,AP是指穿甲弹)
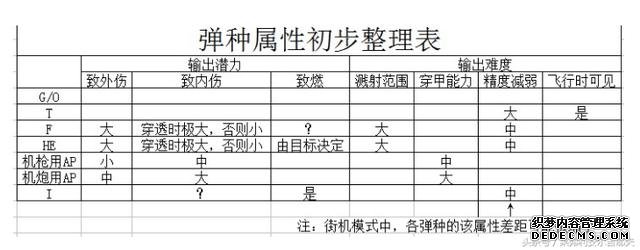
大口径机炮:求击碎靠纯HE或F,求击坠同下↓
其他机炮和大口径机枪:AP+HE或AP+F(如果有的话)> AP+I
小口径机枪:同上,或纯AP
对T/ O/G元素:尽可能少,除非无法保证命中率。
对AP元素:
-1.基本原则:不缺不滥,其在所有弹种中的地位类似一群“0”里的那个“1”。
-2.仅在精确命中时具备很强的致内伤能力。
-3.致外伤能力一般,在以下情况下更低:
(1)外伤触发区面积特别大,如中轴机身结构本身。
(2)外伤触发区装甲硬度低但韧性高,如蒙皮(存疑)。
-4.小口径(7.5-7.7mm)机枪作输出用时,原则上使用标准AP弹,除非发现不这么做也能保证击穿和弹道。
-5.大口径(12.7-15mm)机枪作输出用时,原则上尽量多接纳I/HE/F要素。若发现如此无法保证击穿和弹道,可提高AP元素比重。
-6. 机枪都通过相应配弹用于修正弹道。
对I元素:
-1. 用作输出时:
(1)必须保证弹链中的AP或T数量以保证击穿和弹道。
(2)应尽量保证命中这些部位:
易燃材质制成的机身、油箱(机翼根部?)、引擎(存疑)、机组(存疑)。
(3)最好使用容易命中以上部位的战法,如同向BZ、对头等。
-2. 可用于修正弹道。
对HE/F元素:
-1. 如果作战目标是致外伤,那么该弹种非常合适,伤害极大且不必保证击穿,如果目标易燃还可能点着对方。
-2. 如果作战目标是致内伤:
(1)必须保证弹链中的AP或T数量以保证击穿和弹道。
(2)内伤触发区不像I元素那样受限。
(3)命中区本身存在易燃物时,有致燃效果。
-3. 最适合该弹种的机炮口径,最好超过20mm但不高于30mm,口径在该区间外的机炮,其效果可能不如预期(但很可能依然是最适合该口径机炮的弹种),汉斯线的HEI(武装面板详细信息中名为Minengeschoβ的弹药)不受该限制。
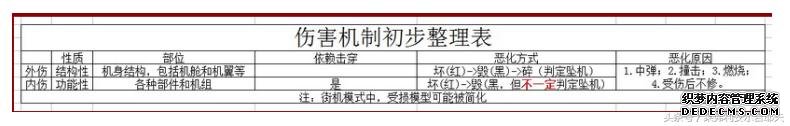
1. 本作中灰机的毁伤,依性质可分为:
(1)内伤,主要为功能性,受伤后将明显影响某项或某些机能。
(2)外伤,主要为结构性,轻伤时不一定有明显影响,但重伤时很可能致命。
2. 前述毁伤都有相应的“伤害触发区”:
(1)内伤区主要对应各种部件、机组,
(2)外伤区主要对应构成机身结构的部分,
预计这些“区”的面积与位置与灰机的对应部分正相关。
3. 本作中多数伤害触发区都在装甲的保护之下,但并非所有装甲覆盖之处都有伤害触发区。
1. 各机的伤害触发区位置、面积、防护能力等。
2. 如何简易判断当前武装能否击穿当前敌机。
3. 每次“击穿”效果是否惠及弹链中的下一颗弹药。
4. 填药比例如何,是否与相应效果成正比。
标准AP弹是一种用钢或硬质合金做弹芯的弹药。其拥有穿甲能力,因此能够对有装甲保护的目标造成伤害,如在200-300米的距离上可以穿透5-8mm的装甲。这种子弹在收拾复杂的飞机组件(引擎,冷却器,操纵系统,武器系统)和机组时效果拔群,在其它情况下则收效甚微,因为那时这种炮弹只能在飞机表面穿个洞后离机飞走而已。在所有弹种中,标准ap弹有最强的穿甲能力,代价是其仅含弹芯,而不填装能引起穿甲以外效果的其它载荷。
API是穿甲燃烧弹。子弹弹头由一个重达1-2g的小燃烧弹构成,它能在穿透装甲的同时,在经过的路径上留下一条火线,这使得API在穿透装甲后可以点燃阻碍物后面的燃料。在游戏中,这种弹药有更高的概率点燃油箱,尤其是没有自动封闭和惰性气体增压的油箱。
AP-T是曳光穿甲弹。这种弹药与AP弹相似,只不过它的底部由曳光物构成。它有穿甲效果,并能留下一条可见的弹道。它的穿甲弹芯质量较小,导致它的穿甲能力较标准的AP弹更低。它的准确度也不如通用弹及标准AP弹,因为其子弹的重量会随着曳光物质的燃烧而改变。
API-T是穿甲燃烧曳光弹。它由穿甲弹芯、燃烧剂和曳光物组成。由于它的通用性,它的穿甲效果和准确度较其它的穿甲弹更低。

In all countries, special armor-piercing shells were designed to counter the deelopment of local armor protecting on aircraft and the need to strike ground target with aircraft cannons. Depending on their action and structure, armor-piercing shells fall into the following categories:
各国都设计了航空机炮所使用的特种穿甲弹,用以对付装甲防护能力日益增强的空中与地面目标。穿甲弹可根据他们的功能结构分为以下类别:
AP for armor-piercing shells; AP表示穿甲弹
AP-T for armor-piercing tracer shells; AP-T表示穿甲曳光弹
API for armor-piercing incendiary shells; API表示穿甲燃烧弹
API-T for armor-piercing incendiary tracer shells. API-T表示穿甲燃烧曳光弹
As far as their structure goes, these shells could be of a solid or caity (a small explosie charge with a base detonating fuse) type, and the explosie charge could consist of an incendiary stick and an explosie stick. The fuse was actiated after it pierced armor of a certain thickness, and the explosie or incendiary effect itself was low, since the explosie charge was considerably smaller than that in fragmentation shells. Bullet of this type work well when fired at complex components, and they are good for striking components with local armor protection, such as armored backrests and armored glass. But they may fly through thinner components, such as the skin, without being actiated, and in this case the enemy aircraft will not be seriously damaged.
说到它们的内部结构,这些炮弹可能是实心弹或有内部装药(含有少量炸药与触发引信),其填药可以由燃药柱和爆药柱构成。引信会在弹药穿透一定厚度的装甲后触发弹体爆炸,爆炸或燃烧的致伤效果很小,因为弹体内的炸药装药量要比破片弹少得多。这种子弹在向飞机上的复杂零件开火时表现优异,也适合打击由装甲覆盖保护的目标,如飞行员座椅背后的防弹钢板,以及防弹玻璃。但是,这种弹药也可能直接保持自身完整地贯通飞机上较薄弱的组件,如蒙皮,而不触发起爆,这使得敌机不会受到严重伤害。
Shells that had increased penetration thanks to a core made of tungsten carbide were used as armor-piercing shells by special-purpose anti-tank BK 37 aircraft cannons.
使用碳化钨作为硬芯以提升穿透力的炮弹,被BK37特种反坦克航炮作为穿甲弹所使用。
Bullets with an incendiary effect wereinitially used in aiation for striking balloons, but practiceshowed that they are also quite effectie at striking aircraft of wooden orcomposite construction.
具有燃烧效果的子弹最早在航空中被用于攻击气球,但是实践证明他们对于打击木质结构与复合结构的飞机也十分有效。
“I” is an incendiary bullet. It carries apayload of highly flammable agents, usually white phosphorus. When it hits thetarget, the incendiary agent ignites it. This bullet has no armor-piercingability.
“I”是一种名为“燃烧弹”的弹药。他通常装填白磷作为高效易燃剂。当他击中目标时,燃烧剂就会被点燃。这种弹药没有装甲穿透能力。
AI is an adjustment incendiary bullet,basically a miniature shell with a primitie impact or time fuse. It is used toaid in directing fire and strike highly flammable targets. When it hitsanything, it produces a bright and highly isible flash, able to ignite fuel intanks that are not protected by armor.
AI 是一种名为“试射燃烧弹”的弹药,概括地说是一种撞击或延时起爆的薄壳弹药。其主要用途是引发燃烧和打击高易燃目标。当其击中任何物体后,会产生一个明亮而显眼的闪光,可以将不受装甲保护的油箱中的燃料点燃。
Schokolade注:AI(试射燃烧弹)是一种介于曳光弹与燃烧弹之间的弹药,可以像燃烧弹一样引燃目标,同时也可以在击中目标时引发明亮的光来提示射手击中目标与修正弹道,在夜间使用能避免常规曳光弹明亮的弹道暴露自己的位置。
High-Explosie Fragmentation Shells

High-explosie fragmentation shells are the primary armament of aircraft cannons These shells hae a steel case filled with an explosie charge and are usually equipped with a point-detonating.direct-action fuse Some shells are filled with a mix of an explosie and an incendiary agent. Depending on the country that produces the bullets and the filling ratio. which is the ratio between the weight of the explosie charge and the total weight of the shell,these shells can fall into the following categories
高爆破片弹为战机航炮的主要弹药,多为钢质外壳内填装高爆炸药,通常配有一个雷管来引爆。一些炮弹混装高爆物质及致燃物质 。根据炮弹的出产国和填药比(即装药的重量和全弹总重之间的比率),可以分为以下类别:
FT for fragmentation tracer shells .
Fl-T for fragmentation incendiary tracer shells .
HEF for high-explosie fragmentation shells .
HET for high-explosie tracer shells .
HEI for high-explosie incendiary shells
FT 破片曳光弹
FI-T 破片燃烧曳光弹
HEF 高爆破片弹
HET 高爆曳光弹
HEI 高爆燃烧弹
These shells cause damage with their shock wae,temperature and fragments .Due to their small filling ratio, shells under 30 mm in calibre had a stronger fragmentation effect .Howeer, special high-efficiency, thin-walled MinengeschoB shells,wilh a much better filling ratio, were deeloped in Geimany. The case of this shell was not turned but solid-drawn, hardened with HF currents. This enabled a considerably larger explosie charge to be placed into the shell. This ammunition worked much better when its target was the aircraft's airframe itself, especially if it was composite, like that of Soiet fighters or the il-2 ground-attack aircraft. Wooden and fabric components would ignite and be destroyed.After the war. the deelopment of small-calibre shells continued in this direction, and similar shells were put into serice in other countries.
上述弹药能通过爆炸产生的冲击波、高温与碎片来造成伤害。由於较少的爆炸物填装比例,低于30mm口径的弹药具较高的破片效果。值得一提的是,德国研发出的:Minengescho β 弹药[译注:似乎为HEI,武装面板弹种详细信息中可查],具有更好的填充率。这种弹药并不是倒空的, 而是整体拉制而成, 并且由高频电流加固。这使得炮弹能容纳的装药,对飞机的机身结构的破坏特别有效,尤其是复合结构的机身(入苏联的战斗机或是IL-2)。其木制结构与布会被点燃,然后灰飞烟灭。战后,这种小口径子弹的配方继续朝这个方向发展与生产,并且被其他国家采用并产生类似的弹药投入使用。
High-explosie fragmentation shells are well suited for destroying the structural components of enemy aircraft,causing a lot of damage, but internal components are not much affected,due to the shells' limited armor-piercing effect: for example, if fired at the engine, the shell would probably be actiated as soon as it hit the skin of the engine cowling, thus not affecting the engine itself .Damage to durable struclural components, such as spars, ribs or cylinders of air-cooled engines, can be caused by
fragments weighing at least 20 g if the shell explodes in immediate proximity to the component. bul a 20 mm shell (weighing 100-150 g) can produce only a small number of such fragments
高爆破片弹[译注:不过本作中有这货么…]适合用于摧毁敌机的机身结构,造成大量的伤害,但由于破片的穿甲能力有限,它不适合破坏飞机的内部结构。举个栗子:如果击中引擎,炮弹会在击中引擎整流罩时就爆炸,而无法伤及发动机的核心部件。伤及翼梁、机肋、气冷引擎的气缸等机身结构组件时,需要至少20g当量的碎片冲击。但是,20mm的弹药(重达100-150g)则只能造成少量的破片冲击,达不到该要求。
来复枪口径弹(7.5-7.7mm)[本文称其为“小口径弹药”]
该弹种滥觞于第一次世界大战。通用弹并不是为打灰机而专门设计的弹药,故其对空效果并不理想,于是当时开始使用燃烧弹打气球和飞艇。之后,当飞机的重量和航速逐渐提高,专用弹药的使用变得更加普遍。
第二次世界大战爆发后,由于全金属飞机投入实战,该弹种的破坏力已经无法满足需求。空战武器向大口径机枪和机关炮的过渡是不可避免的。然而,大量的飞机在第二次世界大战中仍将小口径机枪作为防御性武器,或用于为他们的机炮指示目标。
在苏联,“L”是指定为普通曳光弹,“D”是指定的重型远程的子弹,而同样的弹丸在美国和德国分别被称为“Ball”和“Spitzgeschoβ”。最初,这些种类的子弹设计的目的是射击敌人的步兵。
通用弹具有良好的精度和密度,但是因为穿深不够,使得它们在攻击全金属飞机,或者有装甲的部件时非常无力。
曳光弹(译注:结合本段可知事实上不止“曳光”一种,但由于本作中的T主要为曳光弹,便暂且如此翻译)被指定为“T”。一种特殊的缓慢燃烧的混合物质(称为示踪剂 )被压入其弹头底部,这些子弹在空气中留下了明显的有色踪迹。此外,也存在用于夜间射击的特殊示踪剂。为了防止射手分辨不清,也存在以烟雾示踪的先例,如德国的PMK子弹。其发射后将留下可见的烟雾轨迹,这是由一种被置于子弹底部特殊的树脂产生的。
曳光弹主要用于辅助瞄准和修正弹道。它们很难穿甲,且以曳光弹织出的弹幕密度也比用裸弹(译注:应该指通用弹)更低,这都要归咎于示踪剂逐渐燃尽造成的子弹重量减轻。
Large-Calibre shells(12.7-15mm)
Large-calibre shells had the same types that rifle-calibre bullets did, but when the tracer burned away, it did not influence the accuracy of tracer shells so much due to their larger weight. So, the difference between the penetration of AP-T/API-T and AP shells was not so great when compared with the equialent rifle-calibre bullets. Special-purpose bullets were mainly used, such as AP, API, API-T. In the USSR, adjustment incendiary bullets were designated“МДЗ”(“MDZ”meaning “direct-action incendiary”) or “МД”(“MD”meaning “direct-action”)
大口径弹药与小口径弹药具有相似的作用机制,但当曳光弹(如果有的话)示踪剂烧完之后,它的精度并不会像小口径弹药那样受到严重影响。同理,拜其较大的重量所赐,该口径级别的穿甲曳光弹、穿甲燃烧曳光弹,和标准穿甲弹 之间的穿甲能力差异并不明显。较之于小口径弹药,大口径机枪主要使用特殊弹药,如标准穿甲弹、穿甲曳光弹、穿甲燃烧曳光弹。在前苏联,试射燃烧弹被命名为“МДЗ”[Schokolade注:“МДЗ”为“мгновенного действия, зажигательный”的缩写意为瞬间燃烧](“MDZ”意为瞬间燃烧弹)或“МД”
[Schokolade注:“мгновенного действия”](“MD”意为瞬间)
[Schokolade注:我认为此处为毛子不负责任直接按字母将俄语翻译为英语,如果将“MDZ”和“MD”改为“МДЗ”与“МД”更合理]
总的来说就那么多了,文章有些长,不知道玩家们有没有细心的看完。由于游戏不是中国的,所以很多需要考究的都用了英文或者俄文。所以有些占篇幅,希望谅解。谢谢观看。

